Application Server High Availability Solution
The Application High Availability solution is achieved by multiple server redundancy. If the system contains more than one application server, a Load Balancing (LB) unit routes requests to all active application servers.
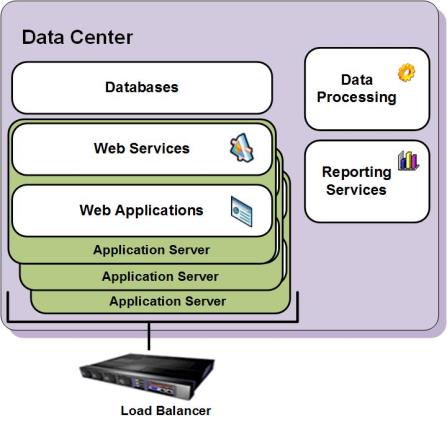
Communication with the application servers is implemented only through the LB virtual address. The system is available as long as one application server is active.
Application server redundancy is also used for system scalability in cases where a single application server is not sufficient to handle the application workload. High Availability solution design must ensure that enough application servers are available at any given time.
For example, in a typical N+1 deployment, the system includes an extra application server in addition to the number of application servers required to process the workload. When not more than one server fails, the system continues to be available and meets the performance requirements. In contrast to the database clustering solution, all application servers are active at all times and are available to serve user requests.
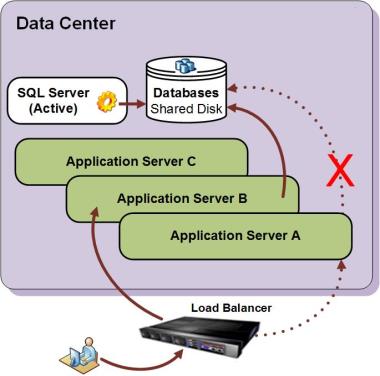
The Application High Availability failover scenario is implemented in the following way:
-
Application Server A fails during an active session.
-
The system prompts the user to log on again.
-
When the user logs on again, the system creates a new session and the Load Balancer directs the session to Application Server B.